Arthritis
Living with arthritis can be challenging, but there are many natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments that can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Explore effective strategies for managing joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation with these holistic approaches.
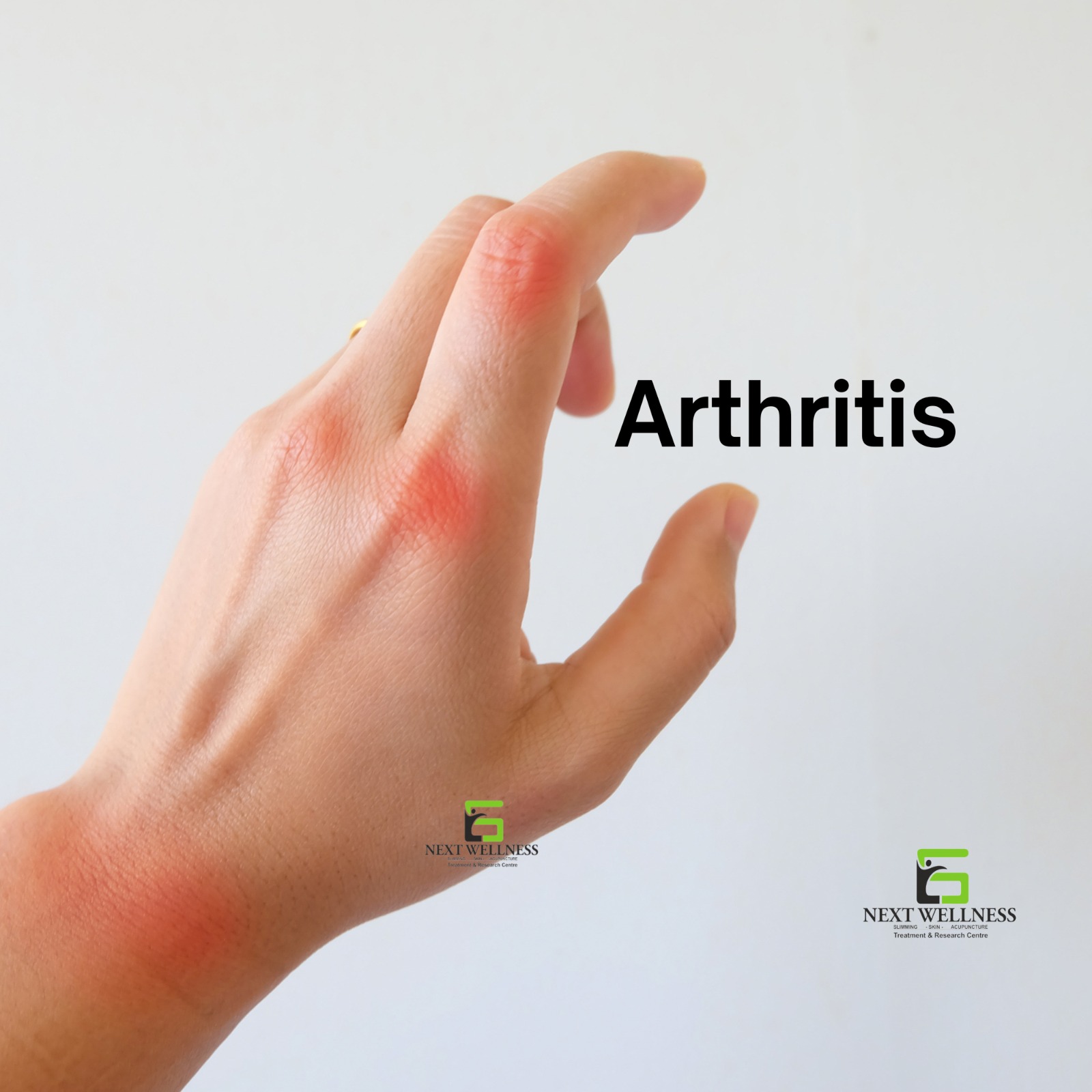
Arthritis
Arthritis is a broad term that refers to inflammation of one or more joints in the body. It's a common condition that affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. The most prevalent types of arthritis include osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Types of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
This is the most common form of arthritis, often referred to as "wear and tear" arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints. OA commonly affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine, as well as the hands.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium (the lining of the membranes that surround the joints), causing inflammation. This inflammation can eventually lead to joint damage, deformity, and erosion of bone and cartilage. RA typically affects multiple joints symmetrically, such as the wrists, hands, knees, and ankles.
Symptoms of Arthritis:
- Joint Pain:
- Swelling:
- Stiffness:
- Joint Instability:
- Joint Deformities:
Persistent or recurring pain in one or more joints is a hallmark symptom of arthritis. The pain may be dull, aching, or sharp and can range from mild to severe.
Inflammation of the joints can cause swelling or puffiness around the affected area. This swelling may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
Arthritis often causes stiffness in the joints, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Stiffness can make it difficult to move the joint or perform daily activities.
Arthritis can weaken the structures that support the joints, leading to a feeling of instability or a sensation that the joint is giving way.
In advanced cases of arthritis, joint deformities may develop, leading to visible changes in the shape or alignment of the affected joints.
Treatments of Arthritis:
- Physical Therapy:
- Surgery:
- Self-care:
- Alternative Therapies:
A physical therapist can help develop an exercise regimen to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion. They may also suggest assistive devices such as braces or splints to support affected joints.
In severe cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical options for arthritis include joint repair, joint replacement (such as knee or hip replacement), or joint fusion to stabilize and realign a joint.
Simple self-care measures such as pacing activities, using ergonomic tools and techniques, and practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing can also help manage arthritis symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Some people find relief from arthritis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or dietary supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin. However, the effectiveness of these treatments varies, and it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying them.
Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Causes:
- Osteoarthritis:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Symptoms:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- Treatment:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- Prognosis:
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
OA is primarily caused by the wear and tear of joint cartilage over time. Factors such as aging, joint injury or trauma, obesity, and genetics can contribute to the development of OA.
RA is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This leads to inflammation, joint damage, and eventually, deformity. The exact cause of RA is unknown, but both genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms of OA typically include joint pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. The pain tends to worsen with activity and improve with rest. OA commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, as well as the hands.
RA is characterized by symmetrical joint inflammation, meaning that joints on both sides of the body are usually affected. Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and fatigue. RA commonly affects smaller joints such as those in the hands, wrists, and feet, but it can also affect larger joints.
Treatment for OA focuses on managing symptoms and improving joint function. This may include medications such as pain relievers and NSAIDs, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications (e.g., weight loss, exercise), and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
Treatment for RA aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, prevent joint damage, and improve overall function. This often involves medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic therapies, corticosteroids, and NSAIDs. Physical therapy and lifestyle changes may also be recommended to help manage symptoms and maintain joint health.
OA is a chronic condition that tends to worsen over time, but its progression can be slowed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Joint damage in OA is typically localized to the affected joint(s).
RA is also a chronic condition, but early and aggressive treatment can help control symptoms and slow the progression of joint damage. Without proper treatment, however, RA can lead to significant disability and deformity.
Nextwellness Treatment & Reasearch Center Pvt Ltd.
Plot no.298 apposite diamond garden, Near merwan cake shop,
Central avenue road Chembur east
MUMBAI 4000-71
Timing: 8 AM to 9 PM
Branch:- Chembur,Bandra.